Cross-Border Payments: What Merchants Should Know

If you’re considering expanding your business internationally, you may be concerned about whether your current payment processing provider is ready for the challenge or not. Not all payment gateways are good at or capable of handling cross-border payments.
It’s a sensible move to step back a bit and review the cross-border payment process and how it truly works before embarking on your global journey. If you’ve already begun, it’s still a good idea to pause and do so before advancing further. It pays to be more informed on how service providers manage cross-border payments once you’ve examined payment processing “behind the curtain.”
If you find yourself asking “what are cross-border payments?”, keep reading! This article will discuss everything you need to know about this popular concept.

Solved: What Are Cross-Border Payments?
Cross-border payments are those in which the payer and the receiver are both located in different countries. Individuals, businesses, and financial institutions wanting to send money across borders can engage in these transactions. Global companies must be ready to receive payments in all the countries they intend to serve.
Cross-Border Transactions Defined
A cross-border transaction is defined as any transfer of property, products, or services involving individuals or businesses from different states. The transaction could be as easy as purchasing widgets from China online or as complicated as multi-tiered joint venture investment arrangements in another jurisdiction with extensive service and distribution contracts.
How Cross-Border Payments Work
Whether a transaction is local or global, cross-border payment processing involves the same seven stages. However, there are some factors to consider in cross-border payments that, if handled properly, will allow you to maximize your international sales. Here’s how:
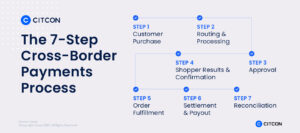
1. The customer purchase: This stage requires more care to make the checkout experience more localized. Always provide the checkout page in the shopper’s native language. Likewise, the pricing of your products should be displayed in the shopper’s national currency. Finally, your checkout page should provide local payment options — no matter where your customer is in the world, they should be able to select the payment method they are most comfortable with. You risk losing the deal if you don’t offer local payment methods online; at the absolute least, your consumer will be unhappy with the transaction.
2. Routing and processing: A payment solutions provider should work with various acquiring banks throughout the planet to better handle cross-border eCommerce transactions. This is because a single-bank arrangement lays the groundwork for global payments to fail. If the acquiring bank is based in the United States and the buyer’s bank is based in another jurisdiction, the transaction is more likely to be detected as fraudulent.
3. Approval: When transactions are directed to the financial institutions that are most likely to accept them, the approval process runs more smoothly. This often includes a suitable geographical match that is compatible with the transaction’s currency and card type.
4. Shopper results and confirmation: When the issuing bank makes a decision, it advises the authorizing bank, which then notifies both the customer and you, the business, via the checkout page.
5. Order fulfillment: This process includes the steps a business takes from the moment an order is received until the moment an order is delivered to the customer.
6. Settlement and payout: Conversion fees, sometimes known as FX fees, are usually charged to merchants who prefer to receive payments in their currency. On the other hand, some providers allow like-for-like payouts, which means they can deposit funds in the same currency as the original transaction into your merchant account. This option will enable merchants to save money on foreign exchange fees.
7. Reconciliation: For companies that receive cash in different currencies, reconciliation can be particularly challenging. For example, a multinational company located in the United States would want Euro transactions to be routed to a bank account that is denominated in euros, Canadian dollar transactions to be routed to a Canadian dollar bank account, and other miscellaneous transactions put into a United States account. If your payment provider offers you easy-to-read processing reports that clearly explain the transaction activity associated with each sort of disbursement, you’ll save time and guarantee accuracy in the process.

Types of Cross-Border Payments
The types of cross-border payments include bank transfers, credit card payments, and alternative payment methods (APMs). Customers prefer paying in a way that suits them. They also want to be given customized options and know that their payment information will be kept safe. As a result, businesses must ensure that all bases are covered and provide various cross-border payment options for their clients.
Bank Transfers
International bank transfers have long been a popular method of making cross-border payments. Many large banks keep a limited number of currencies on hand and will only be able to accommodate a few at a time. As a result, when a UK customer wants to send money to a place where they don’t have the currency in stock, they’ll have to depend on their foreign banking partners to complete the transaction. Smaller banks frequently lack foreign currency reserves and therefore rely on large banks to handle cross-border transactions in their place.
Credit Card Payments
Credit cards are a preferred choice for many people when making cross-border payments. From the consumer’s standpoint, all they need to do is enter their credit card information and wait for the payment to be validated. However, there’s a lot more going on underneath the hood. Since they must convert between two different currencies, cross-border payments demand tremendous effort from the acquiring banks and credit card networks. Additional fees are trickled down the payment chain because of the extra workload.
Mobile Wallet
A mobile wallet is a software-based digital APM that enables clients to pay for transactions either online or in-store. They are frequently offered as smart device applications and let users securely save their preferred payment cards to pay for products and services. PayPal, Alipay, Google Pay, and Apple Pay are just a few examples of popular mobile wallets.
Consumers can use some mobile wallets to transact in several currencies and place orders from different countries. While wallet-to-wallet transactions aren’t precisely cross-border payments, they certainly make the process easier. The transaction is not recognized as a cross-border payment until the funds are taken from the mobile wallet and transmitted to the merchant’s bank account.
Related Read: How to Start Accepting Venmo and PayPal Now Without Delay
Benefits of Cross-Border Payments
You don’t have to look far if you want to learn how international payments can help your business.
You can pay vendors from your phone or other mobile devices via cross-border payments. This allows you to settle an invoice even if you’re not at your desk. Instead of worrying about hundreds or even thousands of invoices, you can leverage your global payments platform to automatically arrange each payment for you, helping you focus on your essential operating activities.
You can connect with more suppliers and affiliates thanks to cross-border payments. For instance, many freelancers are based in other jurisdictions and only charge in their country’s currency. You won’t be able to gain these connections unless you offer cross-border payments. Freelancers can use global payment software and complete a straightforward onboarding procedure that includes entering their payment details. By doing this, they can send you invoices monthly, with automatic reconciliation.
Related Read: How to Collect Payments from International Suppliers
The convenience of managing cross-border payments is probably its most significant advantage, especially with global payment platforms. All payee information is submitted during onboarding and a web interface allows payees to change their information as needed.
Navigating Cross-Border Payment Fees
Cross-border transactions involve several fees to consider. The majority of them are covered by bank charges, which are higher than any other aspect of the transaction. Despite the potentially high cost of cross-border payments, they are in such great demand that they are growing in popularity.
A cross-border charge is among the additional processing fees. This fee is a percentage of the purchase price paid using a foreign credit card. It’s impossible to predict what fraction will be billed in a purchase because this rate varies for each credit card.
However, there is no additional fee charged on top of domestic MDR for mobile wallet cross-border transactions which could be a huge plus for businesses.
Taxes are the greatest unknown since every jurisdiction has its unique tax system. Taxes are imposed on just about everything, including sales tax. Shipments are subject to Value Added Tax (VAT)and customs duty rates, and all these fees differ from one country to the next.
Finally, because every country has its own currency, it is necessary to determine conversion rates. While not an additional cost, the rate is constantly changing, so it’s crucial to keep track of what you’re buying. This has an impact on customers when it comes to purchasing items, but it also has an effect on merchants who receive services across borders.
Related Read: Factors to Consider When Entering a New Market

Cross-Border Payment Solutions
Global cross-border payment flows are estimated to reach US $156 trillion by 2022. This accelerated pace of development in the cross-border payment solutions industry is linked to swiftly shifting consumer demands, growth of emerging markets, and financial inclusion.
Consumers are less inclined to pay for financial services, even if they expect them to be quick and easy. Smartphone adoption and the appeal of online channels for remittances, such as APMs, have introduced new expectations that institutions are striving to meet. Alternative solution providers can achieve a competitive edge over banks by offering quicker, affordable, and more transparent cross-border payment options.
Another key trend in cross-border payments is the increased emphasis on developing economies in Latin America, Africa, and Asia as their share of global transactions grows. Between 2018 and 2022, global cross-border commerce is predicted to raise by about 5% (CAGR) with a majority of this coming from developing countries, which are expected to grow by roughly 11% (CAGR). A case in point is China’s growing eCommerce market.
Furthermore, as mobile phone ownership increases, more people worldwide have access to banking services and e-payment solutions. The percentage of adults in developing economies who own a mobile phone has climbed to roughly 83 percent improving financial inclusion.
How to Accept Cross-Border Payments
With Citcon’s all-in-one payments gateway, you can welcome cross-border business from around the world and make global payments your competitive edge, all while enjoying up to 40% lower acceptance costs than international credit cards.
With additional payment options added regularly, one easy integration enables over a hundred digital wallets and credit cards from providers, such as PayPal, Venmo, WeChat Pay, Alipay, China UnionPay, Kakao Pay, DANA, Gcash, and Alipay HK.
One example is Citcon’s collaboration with China Unicom Global to enable cross-border payments for its newly launched “CUniq” mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) service in the Americas. China Unicom will be able to accept Alipay, WeChat Pay, and Union Pay payments from Chinese travelers and other major credit cards because of this collaboration.
Discover how Citcon’s global payment processing solutions may help you expand your business internationally and gain a competitive advantage. Make an appointment for a free Citcon demonstration today! Call us at +1-888-254-4887 or fill out a demo request form.

