How Do Mobile Payment Systems Work?

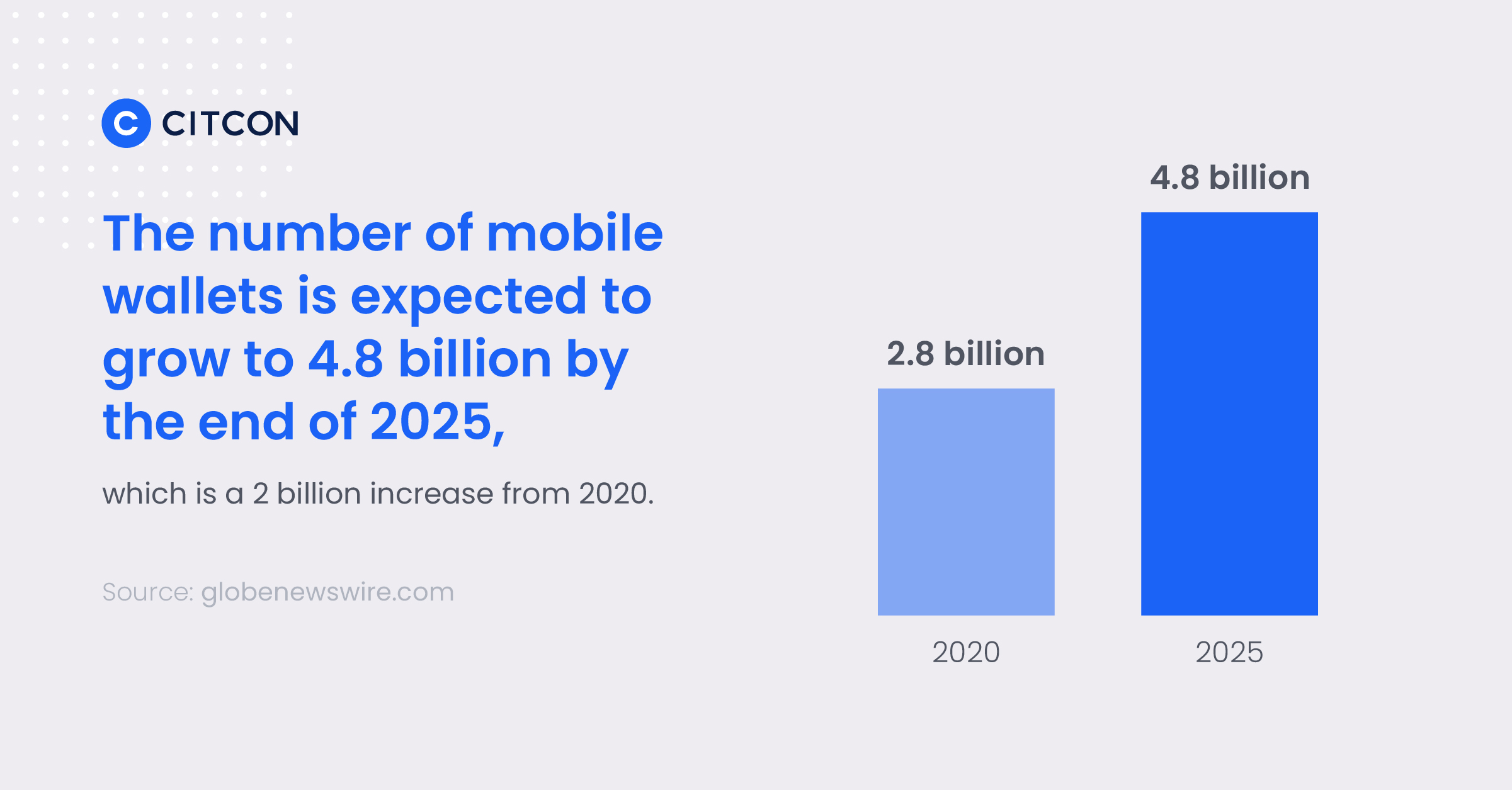
Mobile payment systems are no longer an option for retailers — they’re a necessity. Worldwide, there are more than 2.8 billion mobile wallet users, and that number is expected to grow to 4.8 billion by the end of 2025. Millennials and Gen Z expect mobile payment options, and businesses that don’t meet these expectations will lose sales. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of mobile wallets and take a look at some of the most common types of mobile payment systems.
Understanding Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets are apps that allow consumers to make payments for goods and services directly from their devices. Some of the most popular mobile wallet apps in the United States are PayPal and Venmo.
Related Read: How to Start Accepting Venmo and PayPal Now Without Delay
Mobile wallets are simple for both consumers and merchants to use. Consumers just need to download the app of their choosing and enter their credit card, debit card, or bank account information. This sensitive information is stored securely using tokenization, with the card or account number replaced by a time-limited alphanumeric ID (or token), so the data is never transmitted to or stored by the merchant.
What Is a Mobile Payment System?
For online purchases, mobile wallets offer consumers frictionless checkout. In-store, a mobile payment system offers consumers the ability to make easy and touch-free digital payments using their phone or smartwatch. Initially used primarily in Asia and Europe, mobile payments have been gaining traction in the United States for the past decade.

The growth of in-store mobile payments accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, as both retailers and consumers sought ways to avoid cash transactions, entering PINs by touching shared keypads and handling receipts. In 2020, during the height of the pandemic, mobile payment usage grew by 29% in the United States, with 92.3 million Americans using proximity-based mobile payments and 67% of retailers accepting contactless payments. In 2021, more than four in five Americans used some form of digital payment.
Related Read: Solved: What Does It Cost to Accept Mobile Payments?
7 Types of Mobile Payment Systems
With mobile payments, customers have a touch-free way to pay for purchases in-store, and retailers have a method of accepting payments that don’t require handling cash or cards. Mobile payment systems come in many forms, with some suitable only for point of sale, others for online purchases, and still others that work for both scenarios.
1. Near Field Communication

Near Field Communication (NFC) is a technology that enables the use of contactless payments and mobile wallet apps through radio frequency identification. This form of mobile payment requires a card reader with an NFC chip and a mobile device that also has an embedded NFC chip. These chips can send and receive data when they are near each other.
2. Magnetic Secure Transmission
Magnetic secure transmission (MST) is similar to NFC, but instead of close proximity radio frequency identification, MST uses magnetic signals to allow a device and POS terminal to communicate. This technology is a lot like the magnetic strip used on credit and debit cards, but there’s no card swiping necessary. Instead, MST payment systems involve only a smartphone and a POS terminal that accepts touch-free payments.
MST technology is beneficial in that it can work in scenarios where NFC payments aren’t available, but the growth of NFC adoption has sparked Samsung smartphones to phase out MST.
3. Soundwave-Based
Soundwave-based payments employ state-of-the-art technology to enable touch-free transactions using high-frequency sound waves. A POS terminal transmits sound waves to a customer’s mobile device; the customer’s device converts this data into analog signals and sends sound waves with encrypted payment information to finish the transaction. Like NFC payments, tokenization is used to make these transactions more secure.

An advantage of soundwave-based payments is that they don’t rely on any specific hardware; only an app is needed. Another advantage is that soundwave-based payments don’t require the use of a smartphone or Internet connection; the consumer only needs a standard cell phone with a microphone and speaker.
4. Quick Response Code
By now, most consumers are familiar with quick response (QR) codes. Whether you’re picking up an item curbside at IKEA or dining at your favorite restaurant, you’ve likely used QR codes to read more information about something on your smartphone. Using the camera on your phone, the matrix patterns are decoded and the QR code sends you to a specific URL on your phone’s browser.
Payments via QR code function in a similar way. A customer uses their mobile wallet to scan the merchant’s QR code, then confirm the payment details. Alternatively, a retailer may scan the customer’s QR code on a customer’s phone and finalize the transaction this way.
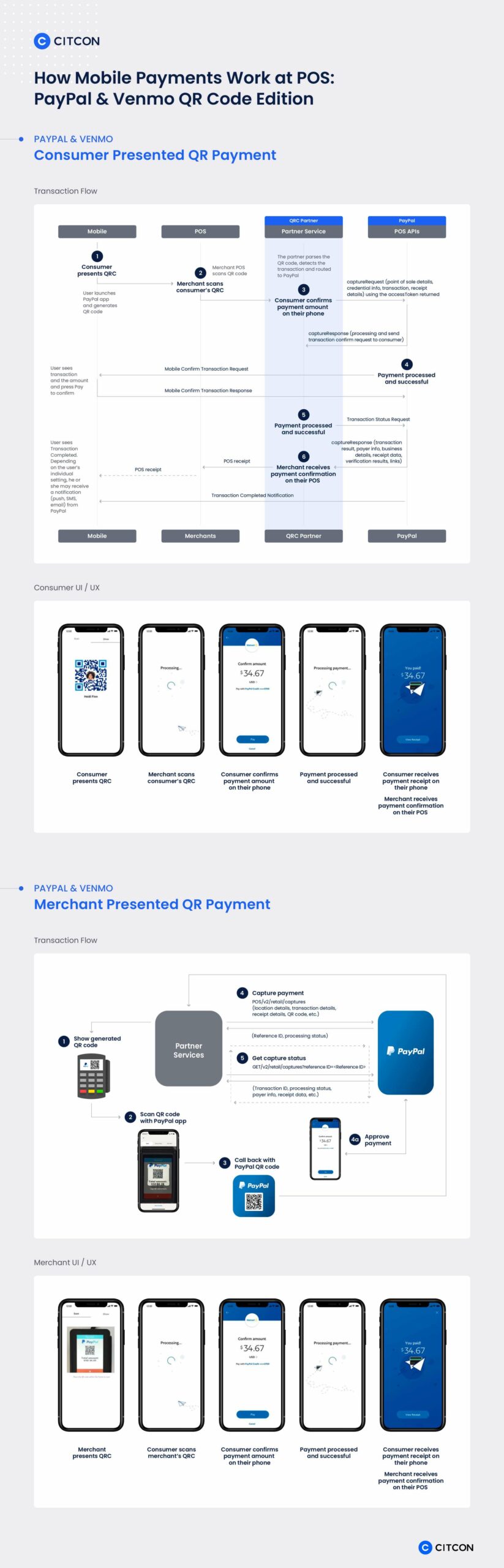
Share This Image On Your Site
5. Payment Link
Payment links involve emailing, texting, or messaging a link to a customer’s device. Once opened, this link leads to a secure webpage where payment details can be entered and the transaction can be finalized. Payment links can be used in chat, email, and invoices.
6. SMS
SMS payments allow mobile users to pay for items or services via text messages. However, an SMS payment differs from a payment link sent by text in that the cost of the purchase is added to the consumer’s mobile phone bill or deducted from a prepaid balance by the mobile phone carrier. SMS payments can take the following forms:
• A customer may get a code from a web page, then text this code to a vendor’s phone number; they will receive a text back confirming payment.
• A customer may enter their mobile number into the retailer’s website; the SMS payment provider texts the customer with a code that can be used to access content online.
• Charities may accept donations by asking donors to send a text to a specific phone number; a text is sent back confirming payment.
This is another simple method that does not require any chips or hardware, but it is primarily used for the purchase of digital items.
7. Bank Transfer
While mobile banking is certainly not new — according to Statista, more than three-quarters of Americans used a mobile device the last time they checked their account balance — an increasing number of mobile banking transactions are person-to-person transfers and payments for bills, goods, and services. Most mobile bank transfers are done through banking apps; users download and create an account on their bank’s app, and from here, they can send bank transfers and payments.
Why You Should Start Accepting Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets have continually gained popularity which was accelerated by the pandemic. We have seen a shift in payment expectations from consumers. They want the convenience, flexibility, and security provided by mobile wallets.
In fact, mobile wallets are the preferred payment option within numerous countries and demographics. For example, credit card penetration is currently less than 10% in India, less than 30% in China, and less than 40% in the EU. As a result, global consumers have adopted alternative payment methods like AliPay, WeChat Pay, PayPal, and other mobile wallets.
In the United States, we are seeing an increase in mobile wallet adoption. As was mentioned, in 2020, mobile payment usage grew by 29% in the US, with 92.3 million Americans using proximity-based mobile payments and 67% of retailers accepting contactless payments.
Whether your business is solely targeting consumers in the US or if you are looking to enter new markets, it is more important than ever to implement mobile wallet payment options at checkout.
Citcon makes it easy to start accepting globally popular mobile wallets. Citcon’s payment gateway enables merchants to accept transactions with more than 100 different payment methods, including mobile wallets, local payment schemes, and traditional credit cards — all through one single integration and reconciliation platform. Some of the mobile wallets we offer include PayPal, Venmo, AliPay, WeChat Pay, as well as buy now pay later services, cryptocurrency, and more.
To learn more about how Citcon helps merchants easily accept mobile wallets, request a demo with one of our payment experts today!



