Cross-Border Payments: 6 Challenges and Solutions

Global e-commerce represents a huge opportunity for U.S. merchants. But what does that mean, exactly? This year, global retail ecommerce sales are expected to reach $5.5 trillion. What’s more, those sales are forecast to jump by almost $2 trillion to a staggering $7.39 trillion by 2025. If you’re considering international expansion, now is the time to take advantage of exponential growth in the global marketplace.
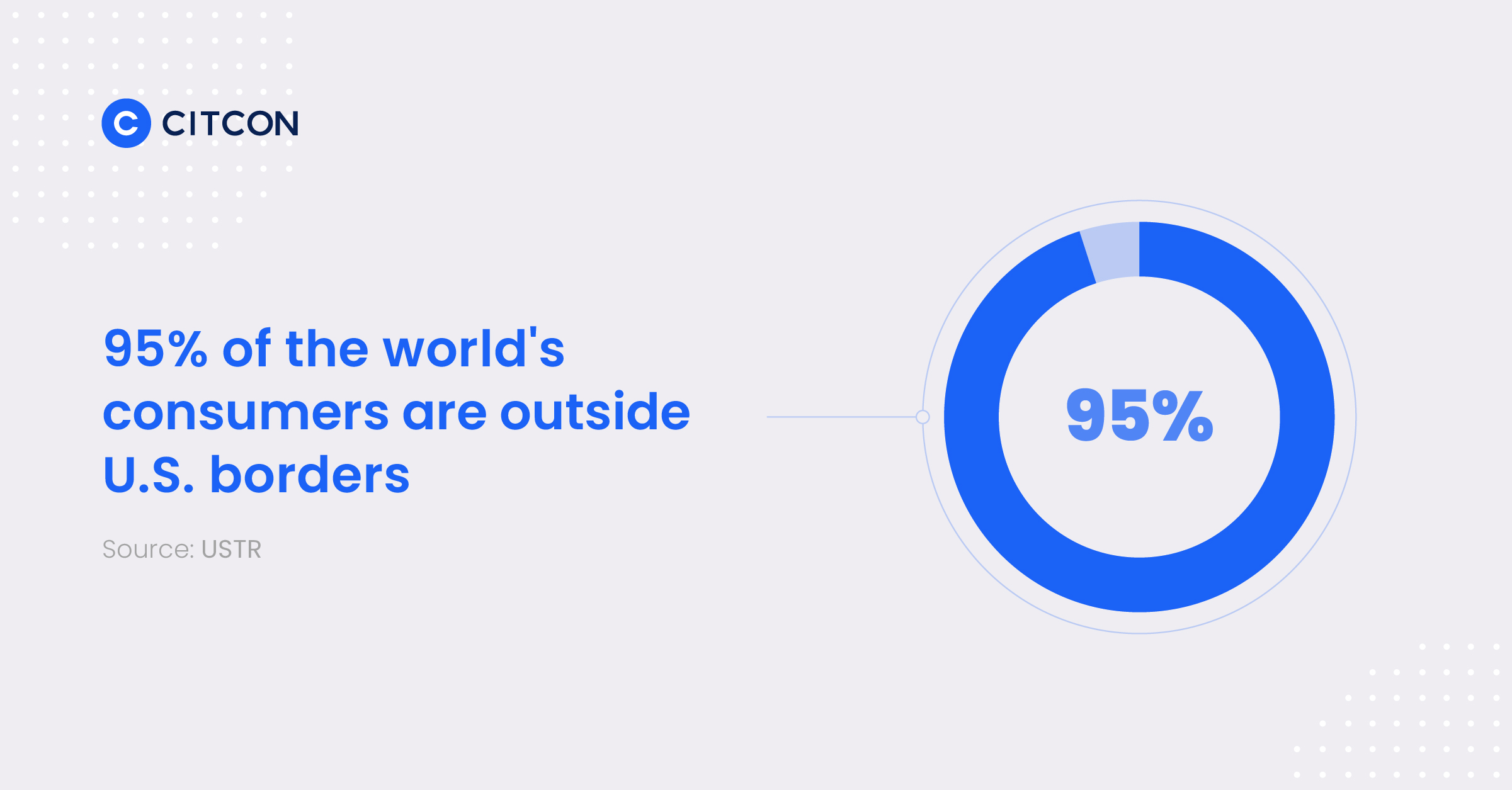
U.S. merchants in particular stand to benefit from borderless retail. The U.S. accounts for less than 5% of the consumer market. This means 95% of the world’s consumers lie beyond the country’s borders.
While cross-border e-commerce is arguably more attractive than ever, challenges do exist. What works at home doesn’t always work in other markets. Even giant retailers have been known to trip while trying to expand globally.
Let’s review some of the common challenges of cross-border payments and what you can do to overcome them.

Overcoming the Top 6 Challenges of Cross-Border Payments
1. Selecting the Right Market(s)
One of the biggest variables in evaluating global regions is how local consumers prefer to pay. Consumers in China, for example, rely heavily on eWallets like AliPay and WeChat Pay for the vast majority of their ecommerce spend (72%). Contrast that with Japan, where credit card penetration is higher, and roughly a third of ecommerce spend is funded by locally issued credit card schemes. Offering payment options customized by region is a strategic way to maximize your impact across various markets. To understand other preferences in your target markets, it’s a good idea to conduct a market segmentation analysis, of which there are a few types to consider. Demographic Segmentation:The easiest segmentation analysis is demographic segmentation, which looks at consumer data like age, education, income, family size, race, gender, occupation and nationality. It provides insights into how different groups buy and use products and how much they spend on them based on demographic considerations. Geographic Segmentation:
A subset of demographics, geographic segmentation deserves its own classification. It’s useful for defining target customer groups based on geographical boundaries. Because consumers have specific needs, desires and interests based on where they live, understanding geographic nuances can help merchants decide what products to sell and how to market them in a new location.
Partnering with a global payments provider with experience in your chosen target market can help you make informed decisions as you expand.
2. Managing Cart Abandonment
Shopping cart abandonment is a well-known challenge for online merchants. It may seem like it’s an unavoidable part of doing business, but there are ways to reduce cart abandonment rates. In Australia, for example, as many as 35% of online buyers reported that they are more likely to abandon a cart if their locally preferred payment option isn’t available. Offering locally preferred payment options is an effective tactic to mitigate cart abandonment and push consumers further down the purchase funnel.
Related Read – The Ultimate Guide on How to Conduct a Cart Abandonment Audit
3. Getting Payments Approved
While average online payment approval rates range from 80% to 90%, those numbers can drop to 50% to 60% when doing business across borders. Why? When a consumer is shopping from an international merchant – and purchase charges originate outside of that consumer’s own country – red flags related to suspected fraud and logistical challenges can lead to declined payments. An effective strategy for improving approval rates is to accept local payments in the markets where you sell. Accepting locally preferred payments will not only attract more customers who rely on these payment forms, but create a smoother transaction experience with far fewer declines for the consumer.
4. Mitigating Fraud, Chargebacks and Fees
The trifecta of international payments woes – fraud, chargebacks and fees — need to be addressed so a business can expand internationally. One way is through mobile wallets. When funds are deducted from a mobile wallet and deposited into the merchant’s bank account in the local currency, the process moves much faster than with traditional credit card payments.
Accepting local mobile wallet payments also allows merchants to bypass card networks, lowering cross-border fees.
5. Optimizing the Checkout Process
Never underestimate the importance of a safe and secure checkout. For example, one in three people in Southeast Asia experienced online fraud while online shopping, as e-commerce and internet activity increased during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The good news? Many locally preferred mobile wallets utilize tokenization to replace sensitive payment information with non-sensitive, randomized strings of characters called tokens. Accepting tokenized mobile wallet payment options offers online shoppers greater safety and security during the checkout process.
6. Localizing Payment Options
Navigating the international payments landscape may feel daunting, but there are resources to help. Partnering with the right payment gateway partner with deep regional expertise can be invaluable to provide the guidance and transparency to meet the needs of your target markets.
Read More About Cross-Border Payments
Take advantage of cross-border e-commerce growth
Discover the best payment methods in Australia and New Zealand
Set up the most popular South Korea payment method
